- Introduction
- 1. 1.Introduction
- 2. 2.A Simple Syntax-Directed Translator
- 3. 3.Lexical Analysis
- 4. 4.Syntax Analysis
- 5. 5.Syntax-Directed Translation
- 6. 6.Intermediate-Code Generation
- 7. 7.Run-Time Environments
- 8. 8.Code Generation
- 9. 12.InterProcedural Analysis
- Published with GitBook
Exercises for Section 3.8
3.8.1
Suppose we have two tokens: (1) the keyword if, and (2) identifiers, which are strings of letters other than if. Show:
- The NFA for these tokens, and
- The DFA for these tokens.
Answer
NFA
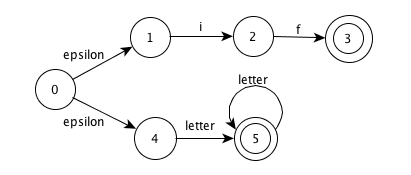
NOTE: this NFA has potential conflict, we can decide the matched lexeme by 1. take the longest 2. take the first listed.
DFA
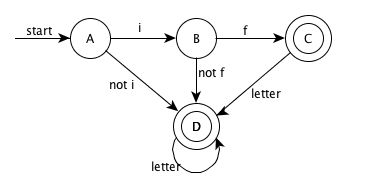
3.8.2
Repeat Exercise 3.8.1 for tokens consisting of (1) the keyword while, (2) the keyword when, and (3) identifiers consisting of strings of letters and digits, beginning with a letter.
Answer
NFA
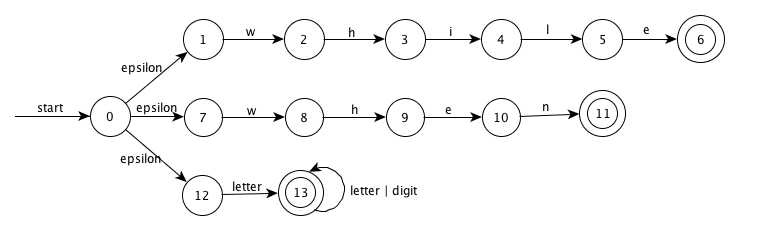
DFA
bother to paint
3.8.3 !
Suppose we were to revise the definition of a DFA to allow zero or one transition out of each state on each input symbol (rather than exactly one such transition, as in the standard DFA definition). Some regular expressions would then have smaller "DFA's" than they do under the standard definition of a DFA. Give an example of one such regular expression.
Answer
Take the language defined by regular expression "ab" as the example, assume that the set of input symbols is {a, b}
Standard DFA
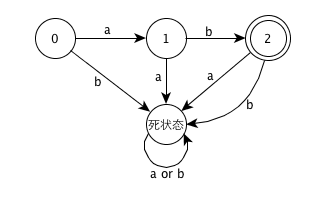
Revised DFA
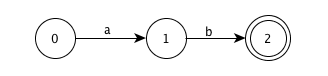
Obviously, the revised DFA is smaller than the standard DFA.
3.8.4 !!
Design an algorithm to recognize Lex-lookahead patterns of the form rl/r2, where rl and r2 are regular expressions. Show how your algorithm works on the following inputs:
- (abcd|abc)/d
- (a|ab)/ba
- aa*/a*